An o-ring is a doughnut-shaped object, or torus. The opposite sides of an o-ring are squeezed between the walls of the cavity or “gland” into which the o-ring is installed. The resulting zero clearance within the gland provides an effective seal, blocking the flow of liquids or gases through the gland's internal passage.
An o-ring is defined by its dimensions (based on inside diameter and cross section), durometer (Shore A hardness), and material composition.
Illustration 3.1 demonstrates three applications showing the two basic categories of o-rings: static – contained within a non-moving gland as in a face seal, and dynamic – contained within a moving gland as in a piston or rod seal.
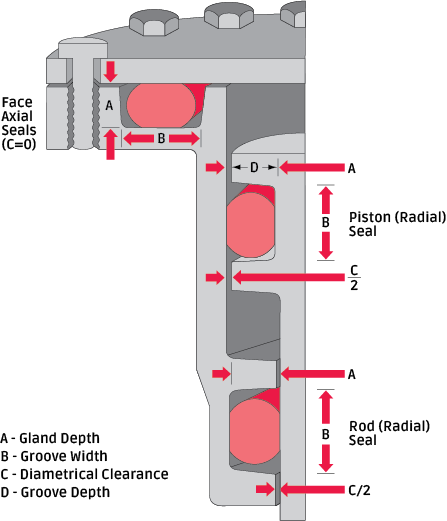
O-Ring Applications